1. Introduction
atural Language Processing(NLP) is a theoretically motivated multiple methods and techniques from which are selected for the accomplishment of particular type of language in analyzing and representing a human communicable at one or more level of linguistic analysis in the purpose of achieving human like languages processing for a range of tasks or applications.
Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD) [2] is the process of differentiating among the senses of words. The process of selecting most appropriate meaning of the word based on the context in which they occur. Computational identification of meaning for words in context is called Word Sense Disambiguation.
WSD [3] process to remove the ambiguity of word in a given context is an important for NLP applications such as Information Retrieval, Machine
2. Approach for Two Word Disambiguation Two Word Disambiguation Rules
Morphological analysis [10], [13] of a word gives detailed information about a word. Morphologically [11] every word carries information with reference to its lexemic form, morpho syntactic [12] category, and inflection. The detailed information may include among many other features, such as root/stem i.e. the lexemic shape listed in the dictionary the lexical category like noun/verb/adjective/adverb/pronoun /number /indeclinable as the case may be.
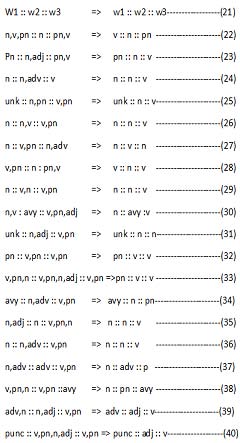
The following are some of the POS tag [4], [5] [6] disambiguation rules [7], [8], [9] used in the task: W1 :: W2 => W1 :: W2
Where W1 and W2 a sequence of words in that order. Where n is noun, v is verb, pn is pronoun, adj is adjective and adv is adverb.
Here from rule 2 when a word carries tags (n,pn) and followed by another word carrying the tag n then the tag pn retained eliminating the n from (n,pn). From rule 10 a word carrying the tag such as (n,pn) followed by avy then most the times pn will be retained and v will be eliminated. Depending on the context linguist will decide which tag will be retained and which one has to be eliminated. These are mostly contextually based syntactic rules. If two word sequences is unable to resolved unique tags then three words, four words sequence rules may be used for disambiguation.
3. III.
Theoritical Explanation with Example for Two Word Ambiguity Here in the above sentence the word carries tags (n,adj) and followed by another word carrying the tag n then the tag adj retained eliminating the n from (n,adj).so from the above sentence adj is eliminated and n is retained.
4. c) After Applying Disambiguation Rule
Adaxi a Nacivewaku alavAtu padipoyiMxi . n n n v punc Where punc is punctuation.
5. d) Analysis of Two Word Disambiguation
Here the below figures 1 and 2 explores the analysis of the Accuracy. Where X-axis indicates the number of test sessions and Y-axis indicates the Accuracy. As the result, we found that the proposal method can disambiguate nearly 98%. :: w2 :: w3 => w1 :: w2 :: w3 n,v,pn :: n :: pn,v => v :: n :: pn In the above sentence the first word carries tags (n,v,pn) and followed by second word carrying the tag n and followed by third word carrying the tags (pn,v) then the tag v retained from the first word and pn retained from the third word eliminating the (n,pn) from (n,v,pn) and eliminating v from (pn,v). iv. Analysis Of Three Word Disambiguation Here the above figures 3 and 4 explores the analysis of the Accuracy. Where X-axis indicates the number of test sessions and Y-axis indicates the Accuracy. As the result, we found that the proposal method can disambiguate nearly 96%.
We are very thankful to all the authors in a reference list, to make this research article in a better shape and right direction.
6. Conclusion and Future Research Direction
This research article explores the impact of twoword disambiguation and three-word disambiguation.
,


| 8 | 926 | n :: v,n :: v,pn | => | n :: n :: v | n :: n :: v |
| 9 | 11634 | n,v : avy :: v,pn,adj => | n :: avy :v | n :: avy :v | |